Understanding Acute Myocardial Infarction: Comprehensive Insights
Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, is a severe medical condition that occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is abruptly cut off, causing tissue damage or tissue death. This medical emergency requires immediate attention, as the health implications can be life-threatening. Through an in-depth exploration of its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, this article aims to provide valuable knowledge for those seeking to understand this critical condition.
Causes of Acute Myocardial Infarction
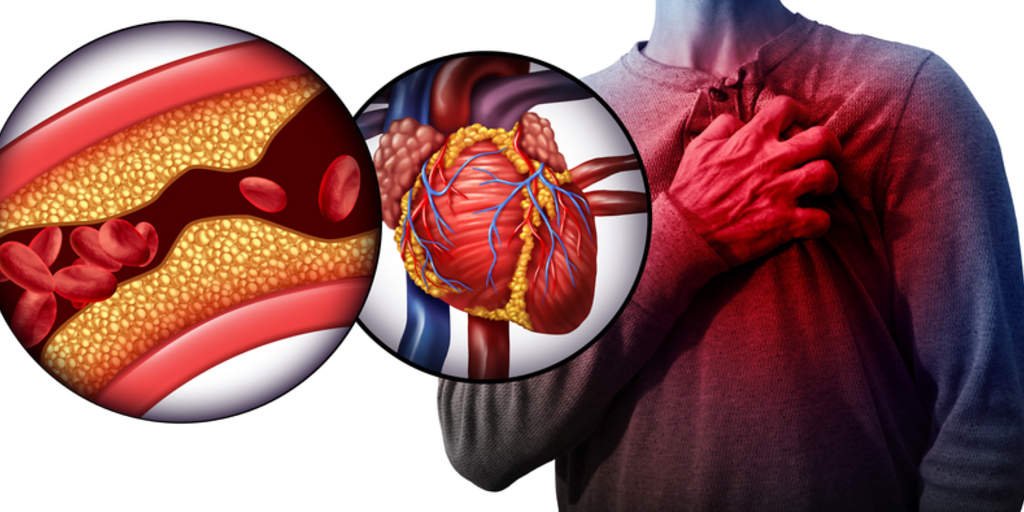
The primary cause of an Acute Myocardial Infarction is the obstruction of coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle itself. This blockage is most often the result of atherosclerotic plaque rupture, a process where plaque, made up of fat, cholesterol, and other substances, builds up on the artery walls. Risk factors enhancing this condition include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and sedentary lifestyle, as well as genetic predisposition. The other rarer causes of acute myocardial infarction are coronary vasospasm and spontaneous coronary artery dissection.
Symptoms of Acute Myocardial Infarction
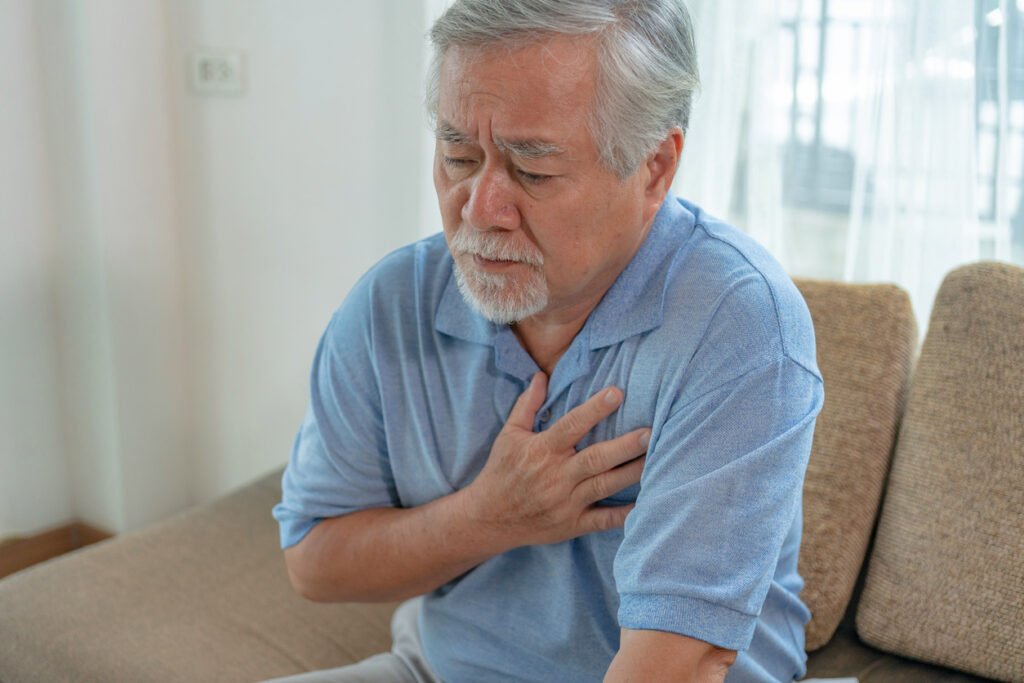

Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack can be crucial for prompt treatment. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort, which may feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of the chest. The pain may last for more than a few minutes or go away and come back. Other symptoms include:
- Discomfort in other areas of the upper body, including arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach
- Shortness of breath, which may occur with or without chest discomfort
- Other signs such as cold sweat, nausea, lightheadedness, or fainting
Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction

Diagnosis of AMI typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examinations, and specific diagnostic tests. Key tests include:
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- This test records the electrical activity of the heart and can identify abnormal heart rhythms caused by a heart attack.
Blood Tests
- Certain enzymes leak into the blood when the heart has been damaged by a heart attack. Measuring levels of these enzymes can help diagnose the condition.
Echocardiography
- This ultrasound test can show whether the heart’s chambers and valves are working correctly and if parts of the heart are damaged.
Treatment Options for Acute Myocardial Infarction

Treatment for AMI aims to restore blood flow to the heart as quickly as possible, minimize heart damage, and prevent complications. Treatment strategies may include:
Medications
- These can include thrombolytics, which help dissolve clots and restore blood flow, antiplatelet drugs, anticoagulants, and pain relievers.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
- Also known as coronary angioplasty, this procedure uses a catheter to place a stent to open up blood vessels that have been narrowed by plaque buildup.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
- Occasionally, this surgery is used after the acute event is stable. This involves using arteries or veins from other parts of the body to bypass blocked coronary arteries.
Preventing Acute Myocardial Infarction

Preventive measures for AMI involve lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medications. Key preventive steps include:
Maintaining a Healthy Diet
Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help reduce heart disease risk.
Regular Exercise
- Engaging in moderate exercise for at least 150 minutes a week can strengthen the heart and improve circulation.
Avoiding Tobacco:
- Smoking and other forms of tobacco consumption are significant risk factors for AMI and other heart conditions.
Regular Health Screenings:
- Monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes management can help catch and mitigate risk factors early.
Living with Acute Myocardial Infarction
Surviving a heart attack requires ongoing management to prevent another occurrence. Rehabilitation programs, regular medical checkups, and adherence to a medication regimen are crucial. Patients may also need to manage anxiety and depression, common issues following such traumatic health events.
Take Action
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a heart attack, it is crucial to seek medical help immediately. For comprehensive care and expert guidance, visit Northern Heart Hospital for more information and support. Remember, the right knowledge and timely action can save lives.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate details of Acute Myocardial Infarction—from its causes and symptoms to diagnosis and treatment—is essential for managing this life-threatening condition. Immediate and effective treatment combined with a proactive approach to prevention can significantly improve outcomes for individuals at risk of or who have suffered a heart attack.
