How to Read Blood Test Results for Heart Disease
Keeping your heart healthy goes far beyond what you feel. Many people walk around with dangerously clogged arteries or damaged heart tissue and feel absolutely fine—until something serious happens. That is why blood tests are so critical in identifying hidden threats before they turn into major problems. Let’s break it all down in this simple, step-by-step guide.
Understanding the Role of Blood Tests in Heart Health
Imagine your blood as a highway that carries not just oxygen, but clues—tiny warning signs that give insight into what’s happening inside your heart and blood vessels. Blood tests allow your doctor to peek inside this highway and detect early signs of heart disease, inflammation, and other risks.
Unlike imaging tests or ECGs that show structural or electrical issues, blood tests give biochemical evidence. They reveal what your cholesterol levels are like, whether you’re inflamed, or if your heart muscle has suffered damage. In other words, blood tests give a molecular map of your heart’s condition.
Why Blood Tests Matter for Cardiovascular Risk
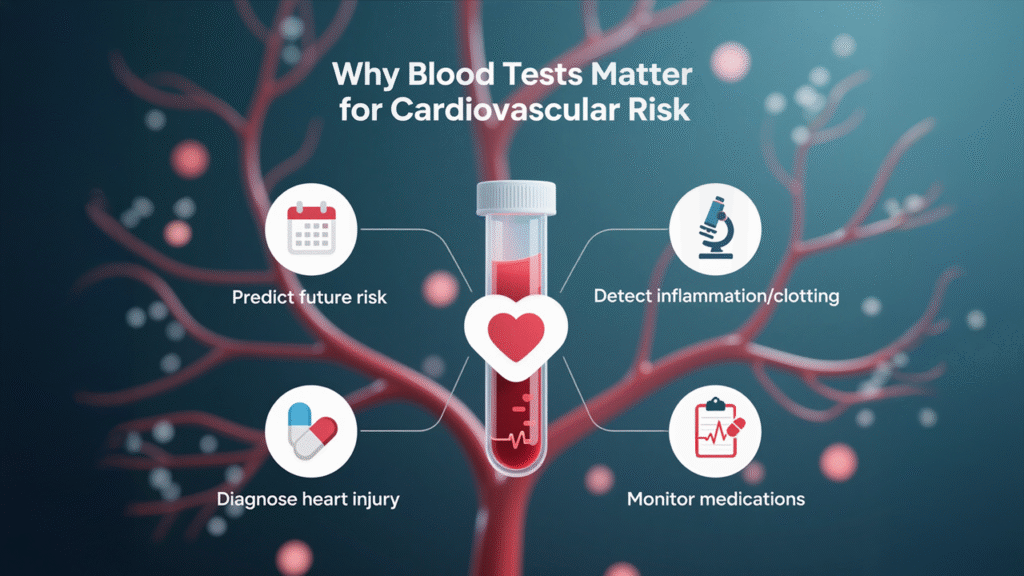
Heart disease often develops silently over time. You may not feel symptoms until there is already significant damage. Blood tests act like an early warning system.
They help in:
- Predicting future cardiovascular events
- Detecting inflammation or clotting risks
- Diagnosing current heart injury
- Monitoring the effectiveness of medication
- Tailoring treatment plans
If you are concerned about your heart or have a family history of cardiovascular problems, getting regular blood tests at a trusted center like Northern Heart Hospital can make a life-saving difference.
Key Blood Markers That Indicate Heart Disease
Let’s walk through the most important blood test components your doctor might order and what each one means.
1. Total Cholesterol
This measures the total amount of cholesterol in your blood. High levels increase your risk of plaque buildup in arteries.
- Normal: Below 200 mg/dL
- Borderline: 200–239 mg/dL
- High: 240 mg/dL and above
2. Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
Often called “bad cholesterol,” LDL sticks to your artery walls, forming plaques that can lead to heart attacks.
- Optimal: Below 100 mg/dL
- High risk: Above 160 mg/dL
3. High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
This “good cholesterol” helps remove LDL from your arteries.
- Ideal: 60 mg/dL or higher
- Poor: Less than 40 mg/dL (men) or 50 mg/dL (women)
4. Triglycerides
These fats in your blood can also contribute to hardening of the arteries when elevated.
- Normal: Below 150 mg/dL
- High: Over 200 mg/dL
5. High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP)
This is a marker for inflammation in the body. Elevated CRP levels are associated with higher risk of heart disease.
- Low risk: <1.0 mg/L
- Average risk: 1.0–3.0 mg/L
- High risk: >3.0 mg/L
6. Lipoprotein(a)
A genetic variant of LDL that’s highly atherogenic. Not part of standard cholesterol tests, but important in those with family history of heart disease.
7. Apolipoprotein B (ApoB)
Better than LDL alone for estimating the number of harmful cholesterol particles.
- Ideal: Less than 90 mg/dL
8. Blood Glucose and HbA1c
High glucose and poor blood sugar control damage blood vessels, increasing cardiovascular risk.
- HbA1c normal: Below 5.7%
- Pre-diabetes: 5.7% to 6.2%
- Diabetes: 6.3% or higher
9. B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP or NT-proBNP)
Used to detect heart failure. High levels indicate that the heart is under stress and pumping inefficiently.
10. Troponin Levels
This is the gold standard for diagnosing a heart attack. Elevated troponin means your heart muscle is injured.
Interpreting Blood Test Results: What the Numbers Mean
Blood test results can look like a confusing string of numbers, but each one tells a story. What matters most is not a single number, but the overall pattern. For example, high LDL, low HDL, and elevated triglycerides paint a very different picture than one abnormal value in isolation.
Always ask your doctor to explain your results in the context of your risk profile, lifestyle, age, and family history.
Patterns That Signal a Problem
Some concerning patterns include:
- High LDL and low HDL: strong predictors of atherosclerosis
- Elevated hs-CRP: inflammation that can destabilize plaques
- High HbA1c with abnormal lipids: sign of metabolic syndrome
- Elevated troponin: immediate red flag for heart attack
- High BNP: points to early or advanced heart failure
Early detection of these red flags through routine checks at Northern Heart Hospital can drastically improve your prognosis.
How Blood Test Results Guide Your Treatment
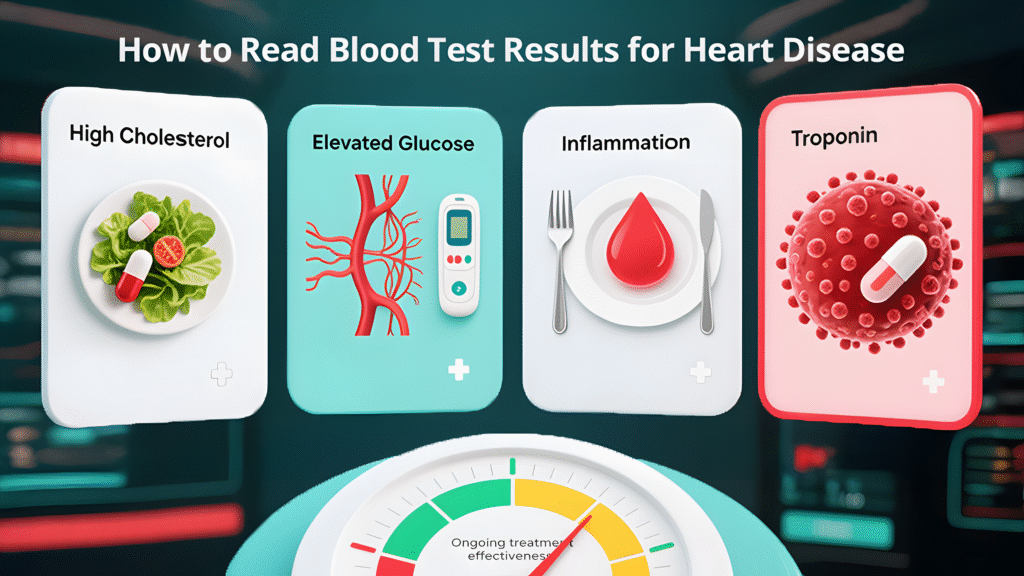
Treatment for heart disease is not one-size-fits-all. Your blood test results act as a compass. For example:
- High cholesterol may call for statins or lifestyle changes
- Elevated glucose suggests better diabetic control is needed
- Inflammation may prompt use of aspirin or other anti-inflammatory measures
- Troponin elevation means urgent hospital care
These results also help measure how well your current treatment is working.
When to Repeat Your Tests
Depending on your health status and risk factors, blood tests might be done:
- Every 5 years (low risk)
- Annually (moderate risk)
- Every 3–6 months (high risk or under treatment)
Ask your cardiologist for a customized schedule, especially if you’re being monitored at Northern Heart Hospital.
Working With Your Cardiologist
Your cardiologist will help you interpret your test results, adjust medications, and recommend lifestyle changes. Be open about your symptoms and habits. The more your doctor knows, the better they can tailor your care.
You can request consultations or follow-up testing directly through Northern Heart Hospital, where experienced specialists are equipped to guide you every step of the way.
How Northern Heart Hospital Can Help You Monitor Heart Health
At Northern Heart Hospital, you will find state-of-the-art testing facilities, leading cardiologists, and personalised care programs. Their comprehensive cardiovascular panel includes the latest diagnostic tools to catch heart disease early—long before symptoms show up.
From advanced blood work to full cardiac evaluations, you’re in good hands.
Final Thoughts: Be Proactive, Not Reactive
Blood tests are not just numbers. They are powerful tools that give you control over your heart’s future. Do not wait until you feel unwell. Use your lab results as a window into your body’s engine and respond early. Because with heart disease, early action is everything.
FAQs: Blood Tests and Heart Disease
1. Can I prevent heart disease with normal blood tests?
Not entirely, but normal results indicate you’re on the right path. They help guide prevention efforts, especially with lifestyle changes.
2. What should I do if one result is abnormal?
Don’t panic. One abnormal value is not a diagnosis. Consult a cardiologist for a full risk assessment and follow-up plan.
3. How long before my blood test results reflect lifestyle changes?
You might see improvements in cholesterol and glucose within 6–12 weeks of consistent diet, exercise, or medication changes.
4. Are home cholesterol testing kits reliable?
They can provide a general idea but are not as accurate or comprehensive as lab testing at facilities like Northern Heart Hospital.
5. Can heart disease exist even with normal cholesterol?
Yes. Inflammation, genetics, or other markers like Lipoprotein(a) or high hs-CRP can still indicate risk even with normal cholesterol.
